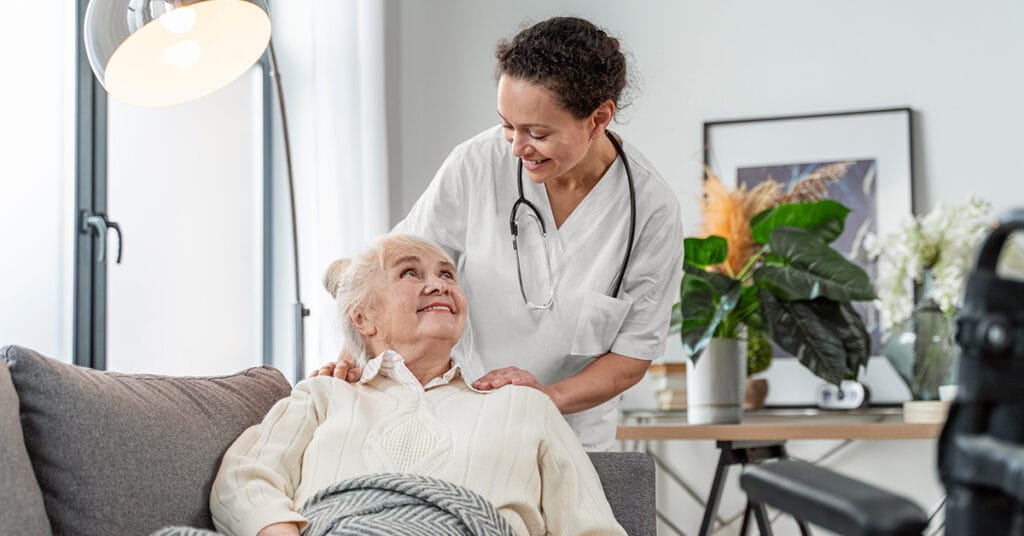
Domiciliary care, often called home care, involves providing professional care and support to individuals in their homes. This service is designed to help people live independently and maintain a high quality of life while remaining in familiar surroundings.
Domiciliary care services are tailored to the individual’s specific needs. They may include personal care (help with washing, dressing, and grooming), household tasks (cooking, cleaning, and shopping), and medical care (administering medications and managing chronic conditions).
One key benefit of domiciliary care is the flexibility it offers. Depending on the level of care needed, carers can visit a few times a week, daily, or even provide 24-hour support. The goal is to help people continue to live independently while receiving the required assistance.
Who Can Benefit from Domiciliary Care?
This can be an excellent option for a wide range of individuals, including:
- Elderly individuals who need help with daily tasks but wish to remain at home.
- People recovering from illness or surgery who need temporary assistance.
- Individuals with chronic conditions such as dementia, diabetes, or heart disease.
- Disabled individuals who need ongoing support for their daily routines.
- Those with mental health conditions benefit from having consistent, compassionate care at home.
Types of Services Provided in Domiciliary Care
Domiciliary care covers a broad spectrum of services, depending on the client’s individual needs. Some of the most common types of support include:
- Personal Care: Help with activities of daily living such as dressing, bathing, grooming, and toileting. Personal care ensures that individuals can maintain their hygiene and dignity while continuing to live at home.
- Companionship and Social Care: Loneliness is a significant issue, especially for the elderly or those living alone. Carers can provide companionship, engage in conversation, and even help the individual participate in hobbies or social activities, promoting both mental and emotional well-being.
- Household Assistance: Help with light housekeeping, meal preparation, grocery shopping, and other household chores. This ensures that clients live in a clean, safe, and organized environment.
- Medication Management: Many individuals require assistance with remembering or correctly administering medications. Carers can help ensure that the right dosages are taken at the right times, which is essential for managing chronic conditions.
- Specialized Medical Care: Domiciliary care can also include more complex medical tasks, such as wound care, catheter management, and assistance with mobility aids. This level of care is often coordinated with a healthcare professional, ensuring the client receives high-quality medical attention at home.

How Domiciliary Care Differs from Other Types of Care
Domiciliary care stands out because it allows individuals to remain in their own homes while receiving care. This is in contrast to more institutional forms of care, such as nursing homes or residential care facilities. Here’s a comparison to help differentiate domiciliary care from other popular care options:
Domiciliary Care vs. Residential Care Homes
- Residential care homes provide 24/7 care in a communal living environment. Residents live at the care home, where they receive round-the-clock assistance with personal care and medical needs.
- With domiciliary care, the individual continues to live at home, and care is provided based on their schedule and needs, which offers a greater sense of independence and privacy.
Domiciliary Care vs. Nursing Homes
- Nursing homes are similar to residential care homes but cater to individuals with more complex medical needs, often requiring constant medical supervision.
- Domiciliary care, on the other hand, offers medical support at home for those who don’t need round-the-clock care but still need help managing chronic conditions or recovery.
Domiciliary Care vs. Live-In Care
- Live-in care involves having a carer move into the home full-time to provide continuous support.
- Domiciliary care offers more flexibility. Carers visit as needed, providing everything from short daily check-ins to longer visits based on the client’s requirements. This allows the individual to maintain more control over their personal space and daily routines.
What are the factors to consider before choosing domiciliary care?
Choosing domiciliary care is a significant decision for individuals and families seeking support for their loved ones at home. There are several key factors to consider to ensure that the care provided meets the specific needs and preferences of the individual. Here’s a guide to the most important factors:
- Assessment of Care Needs: Determine the level of assistance required, such as personal care, medical support, or help with daily tasks. Understanding the specific needs will guide the selection of a suitable care provider.
- Quality and Reputation of the Care Provider: Look for a provider with a good reputation, positive reviews, and relevant accreditations, such as registration with the Care Quality Commission (CQC) in the UK. Ensure carers are well-trained and experienced in handling similar conditions.
- Cost and Affordability: Understand the pricing structure and whether it fits within the budget. Check for eligibility for financial support or government funding to help cover the costs.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The care provider should be able to adjust the level of support as the individual’s needs change. Confirm that they offer services outside standard hours or during emergencies if needed.
- Compatibility with the Carer: The carer’s personality, communication style, and cultural background should align with the individual’s preferences to ensure a positive and comfortable caregiving experience.
Advantages of Domiciliary Care
Domiciliary care is becoming an increasingly popular choice for families looking to support their loved ones while allowing them to stay at home. Here are some key benefits:
- Comfort and familiarity: Remaining in their home means individuals can stay in an environment they know and love. This is particularly beneficial for those with dementia or other memory-related conditions, as familiarity can provide a sense of security.
- Independence and autonomy: Domiciliary care allows individuals to maintain their independence for as long as possible. They have more control over their daily routines, from when they wake up to what they eat for dinner.
- Flexible and tailored support: Care plans are customizable and can evolve as the person’s needs change. This ensures that the care provided is always relevant and appropriate.
- Cost-effectiveness: For many families, domiciliary care can be a more affordable option compared to residential care homes or nursing facilities. Because care is delivered as needed, families only pay for the services they use.
- Emotional well-being: Being able to stay at home and in close contact with family members and friends can significantly improve an individual’s emotional and mental well-being. The support of a domiciliary carer can also reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Conclusion
Domiciliary care provides a flexible, personalized, and cost-effective way to support loved ones while allowing them to continue living in the comfort of their own homes. Whether assisting with daily tasks, personal care, or managing a chronic condition, domiciliary care is an excellent alternative to more traditional forms of care like residential or nursing homes.
If you’re considering care options for yourself or a loved one, this type of care could be the ideal solution to maintaining independence and a high quality of life while receiving the support needed